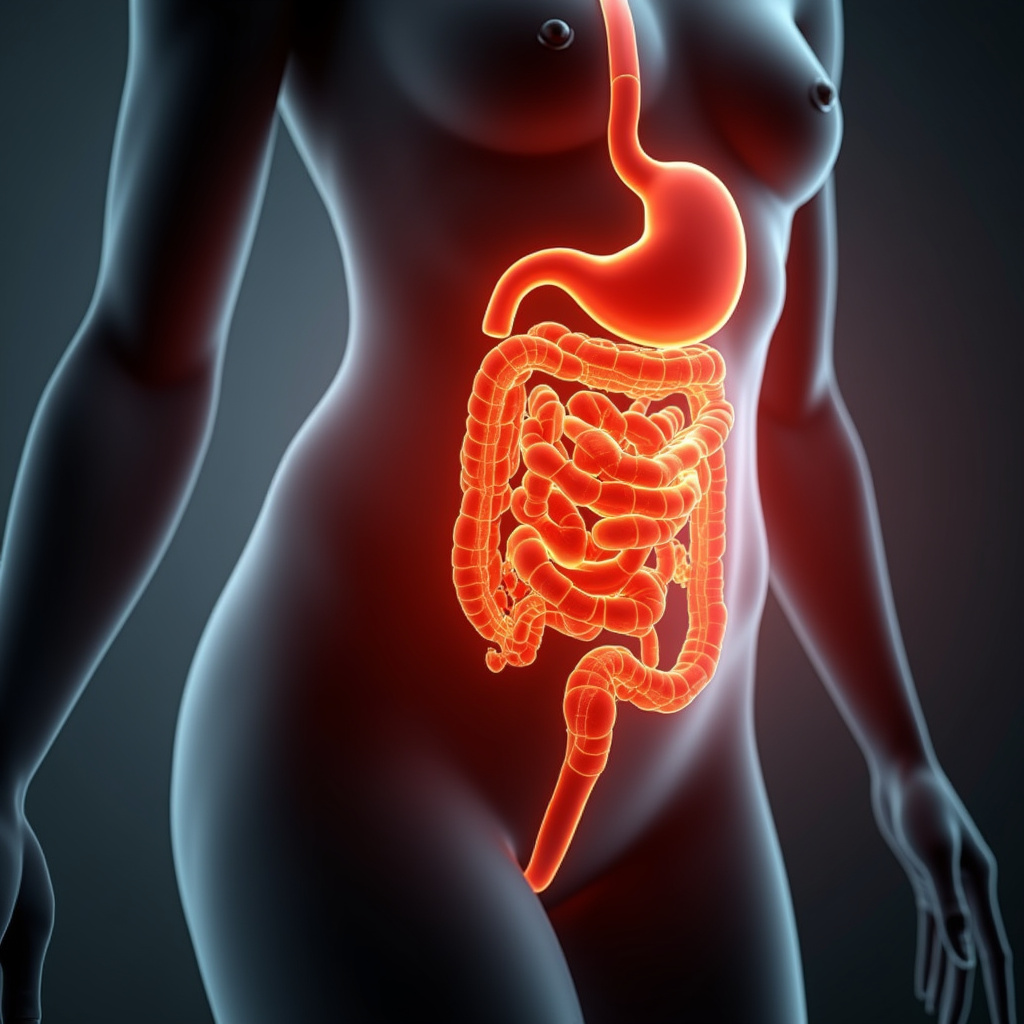
Understanding Insulin Resistance and Abdominal Obesity
What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin resistance is a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When you eat, your body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which enters your bloodstream. Insulin’s job is to help this glucose enter your cells for energy. However, when cells resist insulin, glucose levels in the blood remain high, which can lead to various health issues.
How Insulin Resistance Develops
Several factors can contribute to the development of insulin resistance, including:
- Genetics: A family history of diabetes or metabolic syndrome can increase your risk.
- Poor Diet: Consuming a diet high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can lead to insulin resistance.
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can negatively impact how your body uses insulin.
- Abdominal Obesity: Excess fat in the abdominal area is closely linked to insulin resistance.
Understanding Abdominal Obesity
Abdominal obesity, often referred to as visceral fat, is the accumulation of fat around the organs in the belly area. Unlike subcutaneous fat, which is found just under the skin, visceral fat is more dangerous as it can lead to serious health problems. Measuring waist circumference is a common way to assess abdominal obesity, with a measurement of over 40 inches for men and over 35 inches for women indicating a higher risk.
The Connection Between Insulin Resistance and Abdominal Obesity
Research has shown a strong link between insulin resistance and abdominal obesity. Here’s how they relate:
- Hormonal Imbalance: Excess abdominal fat can lead to hormonal changes that promote insulin resistance. Fat cells, especially those in the abdominal area, release fatty acids and inflammatory substances that interfere with insulin’s action.
- Increased Blood Sugar Levels: As insulin resistance develops, the pancreas produces more insulin to compensate. This can lead to elevated blood sugar levels and eventually type 2 diabetes.
- Metabolic Syndrome: Insulin resistance is a key component of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
Health Risks Associated with Insulin Resistance and Abdominal Obesity
Both insulin resistance and abdominal obesity significantly increase the risk of numerous health issues, including:
- Type 2 Diabetes: Prolonged insulin resistance can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Insulin resistance is linked to high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and an increased risk of heart disease.
- Fatty Liver Disease: Excess fat can accumulate in the liver, leading to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
How to Combat Insulin Resistance and Abdominal Obesity
Fortunately, there are effective strategies to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce abdominal obesity:
- Healthy Diet: Focus on whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit processed foods and sugars.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or strength training, can help reduce visceral fat and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Weight Management: Losing even a small percentage of body weight can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and reduce abdominal fat.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can worsen insulin resistance, so practices like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can be beneficial.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between insulin resistance and abdominal obesity is crucial for maintaining good health. By making informed lifestyle choices, you can take proactive steps to reduce your risk of developing serious health conditions. Remember, small changes can lead to significant results over time, so start today for a healthier tomorrow!