The Connection Between Gut Health and Hormonal Belly
Understanding Gut Health
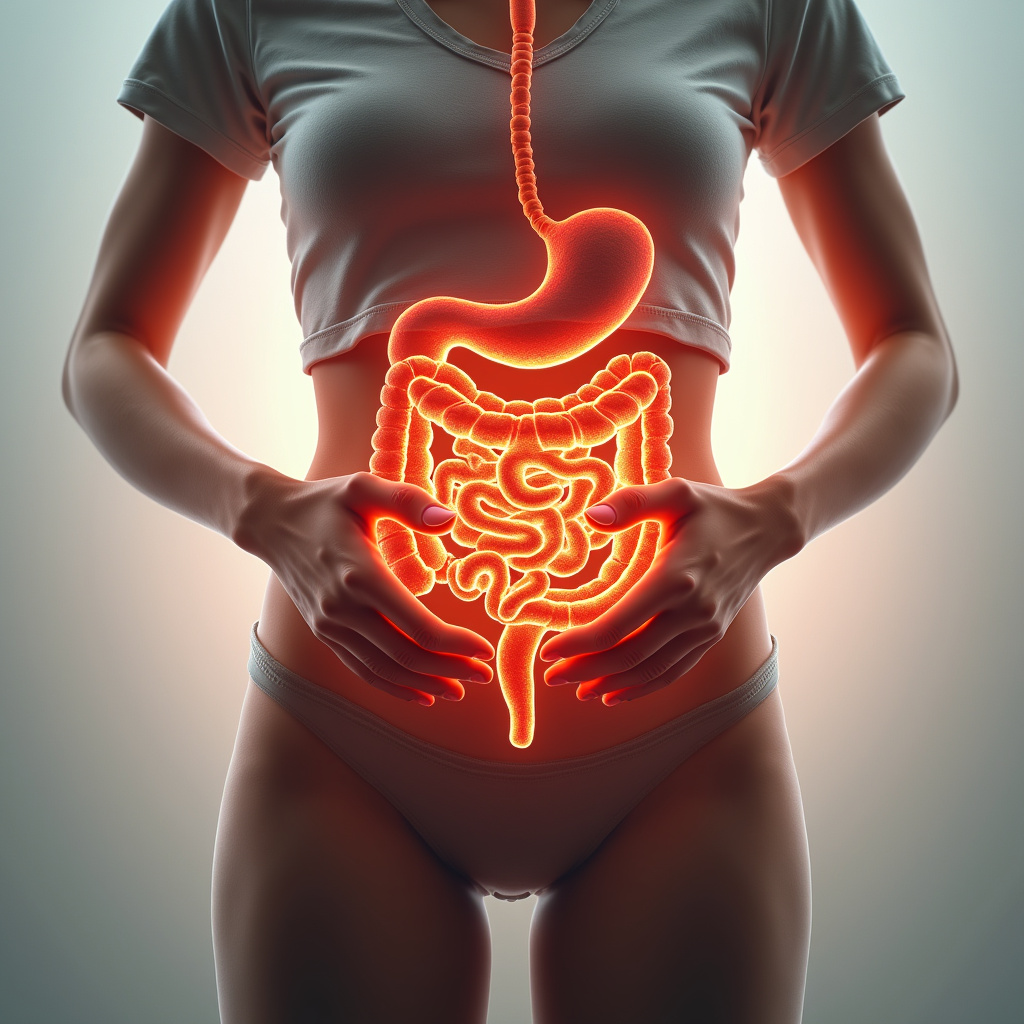
Gut health refers to the balance of microorganisms living in our digestive tract. These microorganisms, known as gut flora or gut microbiota, play a crucial role in our overall health. A well-balanced gut can improve digestion, boost the immune system, and even affect our mood and energy levels. However, when this balance is disrupted, it can lead to various health issues, including weight gain and hormonal imbalances.
What is a Hormonal Belly?
A “hormonal belly” is a term often used to describe weight gain, particularly around the abdominal area, that is influenced by hormonal changes. This type of weight gain is typically linked to hormonal fluctuations caused by factors such as stress, diet, and lifestyle. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), menopause, and thyroid disorders can contribute to a hormonal belly, making it challenging to lose that stubborn fat.
The Gut-Hormone Connection
Recent research has shown that there is a significant connection between gut health and hormone regulation. The gut microbiome influences the production and regulation of various hormones in the body, including insulin, cortisol, and estrogen. A healthy gut can help maintain balanced hormone levels, while an unhealthy gut can lead to hormonal imbalances that may contribute to weight gain.
How Gut Health Affects Hormones
- Insulin Regulation: A healthy gut helps in regulating insulin levels. Insulin resistance, often caused by an unhealthy gut, can lead to weight gain, especially around the belly.
- Cortisol Production: Stress can negatively impact gut health, leading to increased cortisol production. High cortisol levels are associated with fat accumulation, particularly in the abdominal area.
- Estrogen Balance: The gut microbiome plays a role in metabolizing estrogen. An imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to higher estrogen levels, which may contribute to weight gain.
Signs of an Unhealthy Gut
Recognizing the signs of an unhealthy gut can be the first step towards improving both gut health and hormonal balance. Some common symptoms include:
- Bloating and gas
- Unexplained weight gain
- Food intolerances
- Fatigue
- Skin issues
- Frequent infections
Improving Gut Health for Hormonal Balance
Improving gut health can greatly benefit those struggling with hormonal belly. Here are some effective strategies:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your diet. Foods rich in fiber can promote healthy digestion and a balanced gut microbiome.
- Probiotics and Prebiotics: Consider adding probiotics (found in yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods) and prebiotics (found in garlic, onions, and bananas) to your diet. These can help support healthy gut bacteria.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water aids digestion and helps maintain a healthy gut.
- Manage Stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or even simple breathing exercises. Reducing stress can help maintain gut health and hormone balance.
- Limit Processed Foods: Try to reduce your intake of processed foods, as they can disrupt gut health and contribute to inflammation.
Consulting a Professional
If you suspect that your gut health is affecting your hormones and contributing to weight gain, consider consulting a healthcare professional. A doctor or a registered dietitian can provide personalized advice and strategies tailored to your specific needs.
Conclusion
The connection between gut health and hormonal balance is undeniable. By taking steps to improve your gut health, you can help regulate hormones that affect weight gain and overall well-being. Remember, a healthy gut is a vital component of a healthy life!